Descendant Selectors in CSS
Unlock the power of CSS by learning how HTML’s hierarchy shapes every style you apply!
nanadwumor
-
HTML elements form nested parent-child structures.
-
Parents are directly above children; ancestors can be higher up.
-
Descendant selectors style elements inside a parent using a space.
-
Styles affect all matching descendants, regardless of depth.
RECOMMENDED ARTICLES
How to Select Following Siblings in CSS
What if you want to style a paragraph that is far away from a heading but still inside the same container? CSS has a neat trick for that. The [crayon-69b0cff1ccfe5659983891-i/] selector styles elements that come later in the same parent. Elements...
How to Use the Child Combinator in CSS
How to target exactly the elements you want with CSS combinators! > selects direct children only (e.g., h2 > em) Space selects all descendants, any depth (e.g., h2 em) Combinators can be combined (e.g., div.sale p > em) + selects...
nth-of-type Pseudo-class
Learn how to use the nth-of-type() pseudo-class to style specific elements with precision and simplicity. The [crayon-69b0cff1cf59d480382386-i/] pseudo-class selects elements by their position among siblings of the same type. It uses the formula...
CSS uses the structure of HTML document to determine how to apply the styles.
Parent-Child Relationship
HTML is based on hierarchy of elements. Each element in an HTML document is either a parent or child or both. Let’s look at this HTML document:
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 |
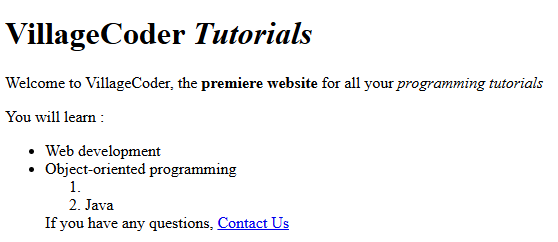
<!DOCTYPE html> <html lang="en-us"> <head> <meta charset="utf-8"> <meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width"> <title>Meerkat Central</title> </head> <body> <h1>VillageCoder <em>Tutorials</em></h1> <p> Welcome to VillageCoder, the <strong>premiere website</strong> for all your <em>programming tutorials</em></p> <p>You will learn :</p> <ul> <li>Web development</li> <li>Object-oriented programming <ol> <li><Python</li> <li>Java</li> </ol> </li> <a>If you have any questions, <a href="mailTo: admin@villagecoder.com">Contact Us</a> </body> </html> |
Output
Parent and Child
A parent element appears above a child element. For example, <head> and <body> are children of the parent element, <html> because they appear below <html>.
<body> is also parent to all first nested elements such as <h1>, <p>, <em>, another <p>, <ul>, <a>.
We have <li> nested in <ol> and this is also nested in <ul>. This makes <ul> a parent of <ol> and <ol>, a parent of <li>. Therefore, <ul> is a grandparent of <li> or <li> is a grandchild of <ul>.
Ancestor and Descendant
An ancestor element is the parent of a descendant element. Therefore, parent/child relationship is a subset of ancestor-descendant relationship. In other words, all parents are ancestors but not all ancestors are parents. In the same vein, all children are descendants but not all descendants are children..
For example, <body> is ancestor of all elements nested within it such as <h1>, <p>, <em>, another <p>, <ul>, <a>.
However, <body> is also a parent of some such as <h1>, <p> because they’re directly under it.
That is, if an element is exactly one level above or below the other, there is a parent-child relationship between them. However, if one element is two or more levels from the other, then there’s no parent-child (direct relationship) but there’s still ancestor-descendant relation.
Descendant Selectors
Space Combinator
Descendant selectors allow you to target elements that are descendants of a specific parent element.
They are represented by writing the parent element followed by a space and then the descendant element. The space is called a combinator. It combines the ancestor and descendant element. The space combinator can be read as “found within” or *a member of “
For example,
|
1 2 3 |
p strong{ background-color : red; } |
will style the background color of all texts in the <strong> element that are also descendants of the <p> element. This means that texts in <strong> that are not descendants of <p> won’t be affected by the style.
This can be read as, apply this style to any <strong> element found in <p>. Or if read from right to left, we say apply the style to any <p> element that is an ancestor of <strong> element.
It’s important to note that descendant selectors will apply styles to all matching descendant elements, regardless of how deeply nested they are within the parent element. For example, <strong> is a 7th descendant of <div> in the code
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 |
<div> <p> <ul> <li>MyStydentClass</li> <li> <ol> <li>FactAlive</li> <li> <a> <strong>VillageCoder</strong> </a> </li> </ol> </li> </ul> </p> </div> |
Because <strong> is a descendant of <div>, no matter the levels between them, it can be styled using
|
1 2 3 4 |
div strong{ font-wieght : 10px; color : yellow; } |
Note that the style affects any <strong> element which is a descendant of <div>.
Also, we could use if we wanted to style specifically the <li> element within <a> within <li> within <ol> within <li> within <ul> within <p> within <div>.
|
1 2 3 4 |
div p ul li ol li a strong{ font-weight : 10px; color : yellow; } |
Combining two or more descendants
You can reach out to any descendant element within an ancestor no matter how deeply nested it is. For example,
|
1 2 3 |
div p a em{ color : yellow; } |
means, apply the style to any <em> element which is found in <a> element and the <a> element found in a <p> element and finally, the <p> element found in a <div> element.
A possible HTML code is,
|
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 |
<div> <p>This is a <a href="#"><em>test</em></a> within a paragraph within a div.</p> <p>This is another <a href="#"><em>test</em></a> within a paragraph within a div.</p> </div> </body> </html> |




Recent Comments